Last update July 10th, 2024 at 05:17 pm
Have you ever wondered who invented solar panels? Although solar technology might seem like a modern invention, the story of solar energy started a long time ago.
The Greeks and Romans used mirrors to focus and reflect the sunlight 300 years BC but it was not until 1839 that the photovoltaic (PV) effect was discovered. The PV effect is the basis of today’s modern solar panels and makes it possible to generate electricity from sunlight.
Let’s take a closer look at solar history. Who invented solar panels, and how long ago?
Charles Fritts: The inventor of solar cells
The American inventor Charles Fritts was the person who made the world’s first solar cells based on selenium back in 1883. Fritts originally hoped that the solar cells he invented could compete with the traditional coal-fired power plants initiated by Edison.
However, the solar cells invented by Charles Fritts were not very efficient, and only 1% of the sunlight that hit the cell was converted to electricity.

Timeline: The history of solar energy
Although Fritts invented solar panels he was one of many who were responsible for making today’s solar energy possible. Fritt’s work and that of many other inventors and scientists throughout the years have made important contributions to the field of solar technology.
Here we will take a look at some important milestones in the history of solar panels.
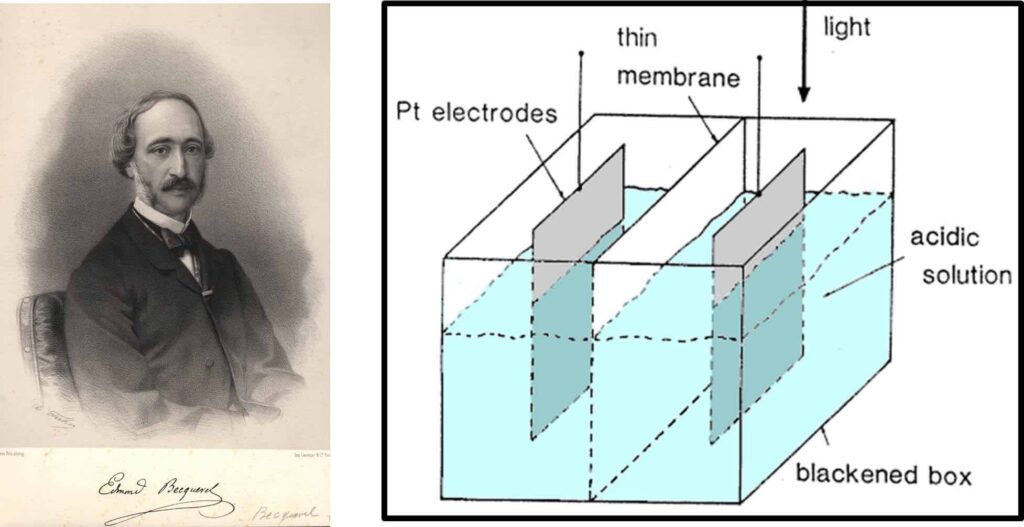
1839: Discovery of the photovoltaic effect
A young Frenchman named Edmund Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect in 1839. Becquerel, who was just 19 years old at the time, experimented with some metal electrodes when discovering the basic physics behind today’s solar cell.
1860s: Solar energy considered a replacement for coal
In the 1860s the Frenchman Augustin Mouchot was looking for a possible replacement for coal as he believed that coal was a finite resource. Importantly, Mouchot could see that coal along with other finite resources like natural gases and oils (fossil fuels) would eventually run out.
Augustin Mouchot invented engines based on solar steam. This solar invention did not use solar panels but instead, it used a parabolic dish concentrating the energy from the sun on a reservoir of water.
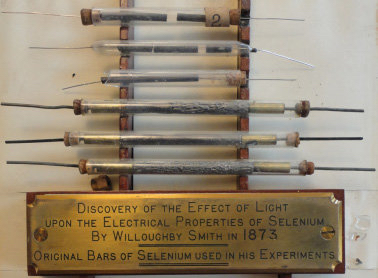
1873: The benefits of selenium were described
In 1873 an electrical engineer from England, Willoughby Smith, described the photoconductive properties of selenium in an article he published. This led to the invention of today’s photoelectric cells, where selenium is often used. The invention of photoelectric cells form the foundation of today’s solar panels.
1876: A demonstration of how light can generate electricity
In 1876, the two Englishmen William Grylls Adams and Richard Evans Day discovered and demonstrated how lightning a junction in between the materials platinum and selenium may cause a photovoltaic effect.
They showed the world that light can actually produce energy and electricity.
1883: First solar cells invented
In 1883, Charles Fritts invented the first solar cells. He made wafers of selenium to do this. This was probably based on Willoughby Smith’s previous descriptions of the material’s photoconductive properties.
1914: Experimental proof of the PV-effect
In 1914, Robert Andrews Millikan, an American physicist, did experiments to prove the photoelectric effect. The experiment was based on Albert Einstein’s description. In 1921, Einstein won the Nobel Prize for his explanation and description of the photoelectric effect.
1953: Calculations of solar efficiency from different materials
Dan Trivich, an American professor, was the first person to calculate what materials were the most efficient ones to use in solar cells. His calculations were based on a number of different materials using different bandgaps.
1950s: Solar cell efficiency increases
Throughout the 1950s solar cells became increasingly efficient. In 1954 Bell Labs invented a solar cell with a 4% efficiency. This would generate enough power to run simple household equipment.
In 1957 Hoffman Electronics produced PV cells with 8% efficiency. By 1960 they were able to increase this number to 14%. In 1958 solar technology was used to power radios in space.
1981: The introduction of solar aircrafts
In 1981 the first aircraft that used only solar power and wind was made by Paul MacCready. The aircraft travelled across the channel between France and England. In the years to come solar technology will become more and more popular.

2008: Residential solar panel systems are getting increasingly popular in Australia
Between 2008 and 2009 the feed-in tariff was introduced in several states of Australia. This made it possible for Australians to earn money (feed-in tariffs) for surplus solar energy that was transported to the grid.
Solar panels today
Today solar panels are very popular in Australia (and the rest of the world). In 2023 as many as 3.7 million Australian homeowners have invested in solar panel technology. This amounts to over 32% of all households in the country.
In recent years the Australian government initiated a solar rebate to make solar panels more affordable for as many as possible. Getting quotes from CEC accredited solar installer is a smart way to get solar on your home.